《C++语言教程》13章 实例指针(this)
“this”是类的实例指针,有一些特殊的用法。
一、参数与成员变量重名
成员函数(包括构造函数)的参数与成员变量重名时,如果不特别指定,则使用的是参数。

#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classca { string id;public: ca(string id) {this->id = id; }voidsetId(string id) {this->id = id; }voidprint() { cout << "id: " << id << endl; } };intmain ( ) { ca a("abc"); a.print(); a.setId("xyz"); a.print();return0; }
二、判断一个对象是否为自己
对象(即实例)可以通过参数传来传去,有时需要判断一下用对象是否与自己是同一实例,可以用“if (&obj == this) { ... }”
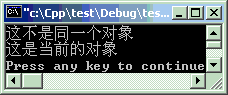
#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classbase {public: void check(base *obj) {if(obj ==this) { cout << "这是当前的对象" << endl; }else{ cout << "这不是同一个对象" << endl; } } };classderive :publicbase {public: base *getBase() { base *p =this; //强制转换成父类的地址returnp; //返回父类地址 } };intmain ( ) { base ba; derive de; base *p1 = de.getBase(); //取基类地址 base *p2 = &ba; ba.check(p1); ba.check(p2);return0; }
三、运算符重载
“this”用于返回自身实例,在运算符重载中经常被使用。
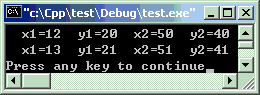
#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classrect {intx1, y1, x2, y2; //矩形座标public: rect() { x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0; } rect(intm1,intn1,intm2,intn2) { x1 = m1, y1 = n1, x2 = m2, y2 = n2; }voidprint() { cout << " x1=" << x1; cout << " y1=" << y1; cout << " x2=" << x2; cout << " y2=" << y2; cout << endl; } rectoperator++() { x1++, y1++, x2++, y2++;return*this; //返回当前实例 } };intmain ( ) { rect r(12, 20, 50, 40); r.print(); rect obj; obj = r++; obj.print();return0; }