《C++语言教程》08章 基类与派生类的构造函数
一、缺省构造函数的调用关系
通过下面的例子,我们来看一下基类与派生的构造函数的调用顺序。创建时先基类后派生类。销毁时先派生类后基类。
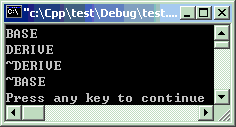
#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classCBase { string name;intage;public: CBase() { cout << "BASE" << endl; } ~CBase() { cout << "~BASE" << endl; } };classCDerive :publicCBase {public: CDerive() { cout << "DERIVE" << endl; } ~CDerive() { cout << "~DERIVE" << endl; } };intmain ( ) { CDerive d;return0; }
二、有参数时的传递
当有参数时,参数必须传送给基类。注意例子中传递的方法(第8行、第19行)。
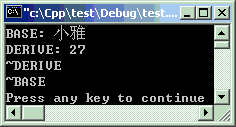
#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classCBase { string name;public: CBase(string s) : name(s) { cout << "BASE: " << name << endl; } ~CBase() { cout << "~BASE" << endl; } };classCDerive :publicCBase {intage;public: CDerive(string s,inta) : CBase(s), age(a) { cout << "DERIVE: " << age << endl; } ~CDerive() { cout << "~DERIVE" << endl; } };intmain ( ) { CDerive d("小雅", 27);return0; }
三、祖孙三代的参数传递
当有三层继承时,参数要一层一层地传递下去(第30行、第19行、第8行)。

#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classCBase { string name;public: CBase(string s) : name(s) { cout << "BASE: " << name << endl; } ~CBase() { cout << "~BASE" << endl; } };classCDerive :publicCBase {intage;public: CDerive(string s,inta) : CBase(s), age(a) { cout << "DERIVE: " << age << endl; } ~CDerive() { cout << "~DERIVE" << endl; } };classCSon :publicCDerive { string id;public: CSon(string s1,inta, string s2) : CDerive(s1, a), id(s2) { cout << "SON: " << id << endl; } ~CSon() { cout << "~SON" << endl; } };intmain ( ) { CSon s("小雅", 27, "8503026");return0; }
四、多重继承的参数传递
多重继承时参数的传递方法和上面一样,要注意的是两个基类的顺序。决定2个基类的顺序是知27行。将27行的CBase1和CBase2的顺序交换一下,其结果中BASE1和BASE2的顺序也随之改变,与第30行无关。
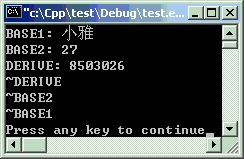
#include<iostream>#include<string>using namespacestd;classCBase1 { string name;public: CBase1(string s) : name(s) { cout << "BASE1: " << name << endl; } ~CBase1() { cout << "~BASE1" << endl; } };classCBase2 {intage;public: CBase2(inta) : age(a) { cout << "BASE2: " << age << endl; } ~CBase2() { cout << "~BASE2" << endl; } };classCDerive :publicCBase1,publicCBase2 { string id;public: CDerive(string s1,inta, string s2) : CBase1(s1), CBase2(a), id(s2) { cout << "DERIVE: " << id << endl; } ~CDerive() { cout << "~DERIVE" << endl; } };intmain ( ) { CDerive d("小雅", 27, "8503026");return0; }