《C++语言教程》16章 new和delete的使用
一、基本数据类型的动态分配
new和delete已经完全包含malloc和free的功能,并且更强大、方便、安全。使用动态分配内存时不能忘记释放内存,不要忘记出错处理!下面先看new和delete的基本使用方法。
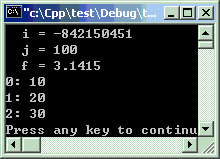
#include<iostream>using namespacestd;intmain ( ) { //基本数据类型int*i =new int; //没有初始值int*j =new int(100); //初始值为100float*f =new float(3.1415f); //初始值为3.14159 cout << " i = " << *i << endl; cout << " j = " << *j << endl; cout << " f = " << *f << endl; //数组int*iArr =new int[3];for(inti=0; i<3; i++) { iArr[i] = (i+1)*10; cout << i << ": " << iArr[i] << endl; } //释放内存deletei;deletej;deletef;delete[]iArr; //注意数组的删除方法return0; }
二、内存分配时的出错处理
一般有2种处理方法,一是根据指针是否为空来判断,一是用例外出错处理所抛出的“bad_alloc”来处理。
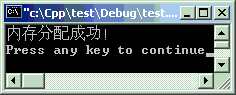
#include<iostream>#include<new>using namespacestd;intmain ( ) { //判断指针是否为NULLdouble*arr =new double[100000];if(!arr) { cout << "内存分配出错!" << endl;return1; }delete[]arr; //例外出错处理try{double*p =new double[100000];delete[]p; }catch(bad_alloc xa) { cout << "内存分配出错!" << endl;return1; } //强制例外时不抛出错误,这时必须要判断指针double*ptr =new(nothrow)double[100000];if(!ptr) { cout << "内存分配出错!" << endl;return1; }delete[]ptr; cout << "内存分配成功!" << endl;return0; }
三、用new产生类的实例
前面章节已经用了很多了。
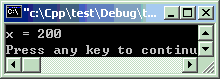
#include<iostream>using namespacestd;classclassA {intx;public: classA(intx) {this->x = x; }intgetX() {returnx; } };intmain ( ) { classA *p =newclassA(200); //调用构造函数if(!p) { cout << "内存分配出错!" << endl;return1; } cout << "x = " << p->getX() << endl;deletep; //调用析构函数return0; }